 |
Berkeley CA (SPX) Feb 07, 2007 Excitement and purpose were palpable today (Thursday, Feb. 1) as the governors of California and Illinois and other speakers addressed a packed press conference announcing the formation of the Energy Biosciences Institute. There was a sense that this new industry-university partnership, to develop and deliver clean, renewable sources of energy, might be a first step toward ending the Age of Fossil Fuels and avoiding global cataclysm. And that's why today was not only "a good day for the University of California, but a really good day for California - and a tremendous day for Mother Earth," said UC President Robert Dynes about BP's selection of UC Berkeley and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory to drive its 10-year, $500 million research initiative, along with the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. The project's focus on renewable biofuels for road transport, along with three other key areas - conversion of hydrocarbons into clean fuels, improved recovery from existing oil and gas reservoirs, and carbon sequestration - will have an "immense positive impact on our world," said BP America Chairman Robert Malone. The institute will be the world's first public or private initiative of this scope to focus on what UC Berkeley Chancellor Robert J. Birgeneau called the "most difficult problem of our time - solving the global energy crisis through technology that avoids damage to our environment." The enormous scale of the project, and the urgency of its mission, places it in the same league historically with the U.S. scientific community's mission to put a man on the moon in the '60s, said Illinois Governor Rod R. Blagojevich. "We can do in biofuels, with the Energy Biosciences Institute, what NASA did for space," he predicted. "When we focus our energies and resources and commitment behind something, we have the innovation and science and technologies to lead the world and get it done," Blagojevich said. Birgeneau agreed, calling the quest for new energy sources that will be not only sustainable, but commercially viable and environmentally friendly, "our generation's moonshot." It is because they are public universities, not private, that UC Berkeley and the University of Illinois are uniquely suited to host this endeavor, Birgeneau emphasized - sharing a mission to address the major problems facing our society. Indeed, Lawrence Berkeley Lab has "already been mounting a full-scale assault on the energy problem for two years," said LBNL Director Steven Chu, in partnership with other research centers and faculty at UC Berkeley. California, which is a global leader in energy efficiency and conservation, is also the right state to mount such an undertaking, said California Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger. He was "immensely proud" that, after looking at university and research institutions all over the world, BP chose California in recognition of its leadership and commitment to clean energy. "California is not waiting for a clean-energy revolution. No - we are actually the leaders in the revolution," said Schwarzenegger, citing California Assembly Bill 32, known as the global warming bill, in which the state pledges to reduce its global warming emissions to 2000 levels by 2010 and eventually to 80 percent below 1990 levels by 2050. California is also a world leader in biotechnology, said BP Chief Scientist Steve Koonin, but he noted that the biotech industry to date has been largely focused on biomedicine and the development of pharmaceuticals. Fewer applications have emerged for the chemical and agricultural industries, but the new biosciences institute will likely produce major advancements for both in the quest for new, more efficient biofuels. Given the University of California's track record in what Dynes called "research, development, and delivery, or RD and D," Koonin expects progress to be rapid. And in addition to its arsenal of research expertise, UC Berkeley is the right partner "to anticipate and manage the social impacts of large-scale biofuels production," he said. "It's time for us to get to work." Community Email This Article Comment On This Article Related Links UC Berkeley Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Civil Nuclear Energy Science, Technology and News Powering The World in the 21st Century at Energy-Daily.com Our Polluted World and Cleaning It Up China News From SinoDaily.com Global Trade News The Economy All About Solar Energy at SolarDaily.com Powering The World in the 21st Century at Energy-Daily.com
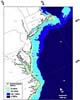 Stanford NY (SPX) Feb 06, 2007
Stanford NY (SPX) Feb 06, 2007The wind resource off the Mid-Atlantic coast could supply the energy needs of nine states from Massachusetts to North Carolina, plus the District of Columbia--with enough left over to support a 50 percent increase in future energy demand--according to a study by researchers at the University of Delaware and Stanford University. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2006 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA PortalReports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additionalcopyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |