 |
Washington (UPI) May 31, 2010 The explosion on Transocean's Deepwater Horizon rig in the Gulf of Mexico and subsequent torrent of oil pouring into the gulf could be the United States' worst environmental catastrophe. Possibly hundreds of billions of dollars of damage will result, let alone the undetermined consequences for flora and fauna. Meanwhile, Washington will be hard at work playing the blame game from BP, which operated the rig, to the White House. But will anything be accomplished let alone learned? Aside from a few Democrats blaming George Bush, Dick Cheney and their energy policies for causing this disaster, some Republicans calling this incident President Barack Obama's "Katrina" and shrewder journalists wondering whether this will be akin to Jimmy Carter and the Iranian hostage crisis of 30-odd years ago, there is a more serious lesson to be learned. Consider this spill the environmental equivalent of Sept, 11, 2001, in reminding us of the fragility and potential vulnerability of our society to acts of man. In coming days, the oil spill will be used as a warning of other potential disasters from crippling cyberattacks that bring the nation to its knees to how Greece's debt crisis will provoke another financial meltdown. Fortunately, so far, none of the key figures at BP, Transocean and Halliburton, the companies ensnared in this drama, has been tainted with any Taliban or al-Qaida connections. Imagine what a stir that would cause. So what should be done? Facts matter. The first step must be a credible and objective assessment of what caused this spill; who was responsible and culpable; what the damage is likely to be; what additional oversight and inspections are required and who will make them; and how the responsible companies will provide fair restitution. This analysis would be aided by evaluation of the impact of oil seeping naturally into the oceans through the Earth, a much greater contributor to spills than any man-made event. Obviously, this doesn't help residents of the gulf whose livelihoods could be ruined or severely harmed. However, such knowledge of these greater leakages could provide a better context for evaluation of the gulf spill. The larger concern is national security. No matter how rich and robust our economy is, real and potential fragilities and vulnerabilities always exist. From Y2K, in which computer networks were predicted to fail as internal calendars clicked over from 1999 to 2000, to the latest swine flu or pandemic scare, we are reminded of our potential weaknesses. This spill reaffirms the urgent need to review the critical soft and hard points of society and to determine how to and who should protect them. Unfortunately, the track record of public and private sector watchdogs is at best uneven. No one in the government regulatory agencies, for example, detected the indicators of the financial and banking meltdowns. Despite the ocean of money poured into homeland security, there was an attempt to bomb an airliner over Detroit last Christmas and a car bomb was left in Times Square after suspects in those cases eluded counter-terrorist surveillance. And of course the Department of Interior's Mineral Management Service won't escape culpability for the spill. Given the gulf disaster, BP, Transocean and Halliburton have fared no better in oversight or inspection. But the same was true of the great Wall Street banks that collapsed. Hence, one conclusion that must be re-emphasized is that oversight is essential to national security -- not merely protecting the nation from attack but preventing catastrophes from happening. During the Clinton years, an infrastructure vulnerability study was commissioned. Little real corrective action followed. In the narrower case of catastrophe prevention through tougher oversight and inspection, we need to understand how the appropriate regulatory bodies can be strengthened, changed or given the authority to match assigned responsibility. This applies throughout government and the private sector and as much to the Securities and Exchange Commission and the Interior Department as to the finance, energy and information industries. Unfortunately, a dysfunctional and septic political process in which blame, allegations of wrongdoing and innuendo dominate and pass for debate, isn't the best venue for establishing corrective action. Partisanship will intensify in an election year. Politics will harden even more in that "you are either with us or against us." But it is time to wake up. We have had September 11. We have had a financial and economic meltdown. And now we have this disaster in the gulf. Each was man-made. No regulatory regime, private or public, is perfect or fail-safe. Accidents and acts of nature are inevitable. However, if government is to be serious and effective in safeguarding the public, leadership is desperately needed to deal with these and other potential crises that can do inestimable damage to the nation and the globe. This catastrophe isn't to be wasted. (Harlan Ullman is chairman of the Killowen Group, which advises leaders of government and business, and senior adviser at Washington's Atlantic Council.) (United Press International's "Outside View" commentaries are written by outside contributors who specialize in a variety of important issues. The views expressed do not necessarily reflect those of United Press International. In the interests of creating an open forum, original submissions are invited.)
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Powering The World in the 21st Century at Energy-Daily.com
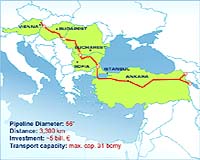 Emirates looking to add to Nabucco
Emirates looking to add to NabuccoAbu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates (UPI) Jun 2, 2010 The United Arab Emirates is moving into position as a possible partner in the planned 2,100-mile Nabucco pipeline to pump natural gas from the Caspian Basin to Europe. The Emirates is using its $328 billion sovereign wealth fund to invest in energy-rich Turkmenistan, which has the world fourth largest has reserves. It recently took the strategic decision to diversify its gas expo ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |