 |
Pittsburgh PA (SPX) Jun 27, 2007 Deep coal seams that are not commercially viable for coal production could be used for permanent underground storage of carbon dioxide (CO2) generated by human activities, thus avoiding atmospheric release, according to two studies published in Inderscience's International Journal of Environment and Pollution. An added benefit of storing CO2 in this way is that additional useful methane will be displaced from the coal beds. Finding ways to store (sequester) the greenhouse gas CO2, indefinitely, is one approach being investigated in efforts to reduce atmospheric CO2 levels and so help combat climate change. CO2 might be pumped into oil wells to extract the last few drops of oil or be placed deep underground in brine aquifers or unmineable coal seams. Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's National Energy Technology Laboratory have carried out initial investigations into the potential environmental impacts of CO2 sequestration in unmineable coal seams. The research team collected 2000 coal samples from 250 coal beds across 17 states. Some sources of coal harbor vast quantities of methane, or natural gas. Low-volatile rank coals, for instance, average the highest methane content, 13 cubic meters per tonne of coal. The researchers found that the depth from which a coal sample is taken reflects the average methane content, with much deeper seams containing less methane. However, the study provides only a preliminary assessment of the possibilities. The key question is whether methane can be tapped from the unmineable coal seams and replaced permanently with huge quantities of carbon dioxide; if so, such coal seams could represent a vast sink for CO2 produced by industry. The researchers point out that worldwide, there are almost 3 trillions tonnes of storage capacity for CO2 in such deep coal seams. To replicate actual geological conditions, NETL has built a Geological Sequestration Core Flow Laboratory (GSCFL). A wide variety of CO2 injection experiments in coal and other rock cores (e.g., sandstone) are being performed under in situ conditions of triaxial stress, pore pressure, and temperature. Preliminary results obtained from Pittsburgh No. 8 coal indicate that the permeability decreases (from micro-darcies to nano-darcies or extremely low flow properties) with increasing CO2 pressure, with an increase in strain associated with the triaxial confining pressures restricting the ability of the coal to swell. The already existing low pore volume of the coal is decreased, reducing the flow of CO2, measured as permeability. This is a potential problem that will have to be overcome if coal seam sequestration is to be widely used. The research team has also investigated some of the possible side-effects of sequestering CO2 in coal mines. They tested a high volatility bituminous coal with produced water and gaseous carbon dioxide at 40 Celsius and 50 times atmospheric pressure. They used microscopes and X-ray diffraction to analyze the coal after the reaction was complete. They found that some toxic metals originally trapped in the coal were released by the process, contaminating the water used in the reaction. "Changes in water chemistry and the potential for mobilizing toxic trace elements from coal beds are potentially important factors to be considered when evaluating deep, unmineable coal seams for CO2 sequestration, though it is also possible that, considering the depth of the injection, that such effects might be harmless" the researchers say. "The concentrations of beryllium, cadmium, mercury, and zinc increased significantly, though both beryllium and mercury remained below drinking water standards." However, toxic arsenic, molybdenum, lead, antimony, selenium, titanium, thallium, vanadium, and iodine were not detected in the water, although they were present in the original coal samples. Email This Article
Related Links
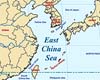 Tokyo (AFP) Jun 26, 2007
Tokyo (AFP) Jun 26, 2007Japan and China on Tuesday failed to break the deadlock in a longstanding dispute over drilling rights in the energy-rich East China Sea in their latest round of talks, officials said. The Asian rivals' one-day meeting in Tokyo, the ninth round of talks since the dialogue began in 2004, ended without tangible results and with no fresh formal proposals from either side, Japanese officials said. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2006 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA PortalReports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additionalcopyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |